Ansible is open-source software that automates software provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment.
Ansible connects via SSH, remote PowerShell, or via other remote API and it is now one of the basic requirements to run the Ansible job through CI tools such as Jenkins to automate the server provisioning and configuration.
This helps developers and other users to directly run specific jobs without the deep knowledge of Ansible.
In this detailed guide, we will show you how to run Ansible Playbook from Jenkins using three different methods.
So, if you want to learn how to integrate Ansible with Jenkins, this is the complete step-by-step process (with screenshots).
Run Ansible Playbook from Jenkins: Your Options
You can run the Ansible playbook through Jenkins in multiple ways:
- Method #1. Using default method which needs Ansible to be configured on Jenkins Master: best and the recommended method to run Ansible job.
- Method #2. Executing Ansible playbook as Shell command or Windows batch command: can be used for testing purposes to run Ansible Playbook on remote host.
- Method #3. Running Job on a separate Node/Agent where you can install Ansible: suited to cases where Jenkins master doesn’t allow Ansible installation or is already having performance crunch.
How to Run Ansible Playbook from Jenkins: Step-by-step
Let’s start with the recommended way to run the Ansible playbook with Jenkins Job or Jenkins Pipeline.
Method #1. Using Default Method (Ansible Configuration on Jenkins Master)
Pre-requisites:
So, the very first step to use the Ansible module in Jenkins is to install and configure Ansible in Jenkins.
Step #1. Install Ansible Plugin in Jenkins
To use Ansible and run Ansible’s playbook through Jenkins, you need to:
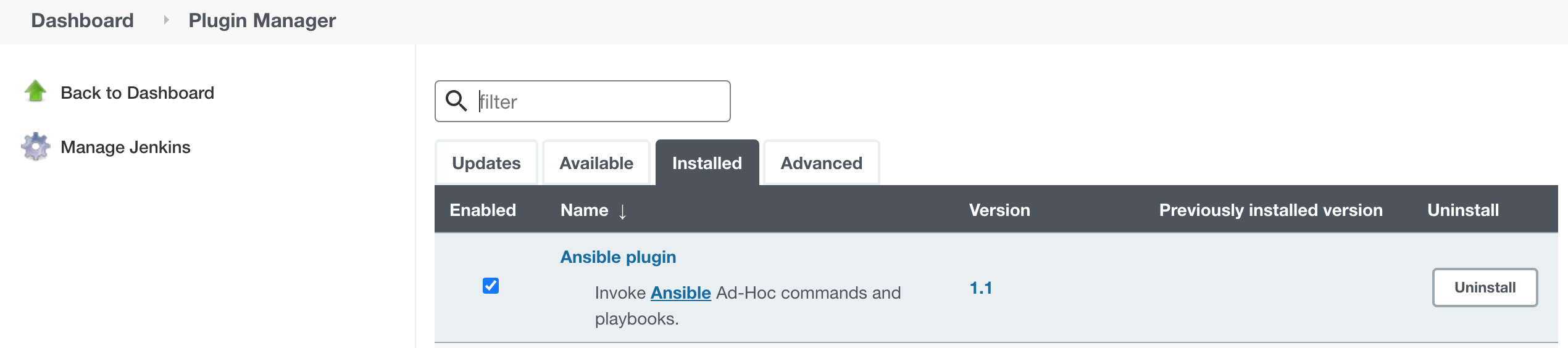
Install Ansible Plugin, Go to Manage Jenkins.
Go to Manage Plugins.
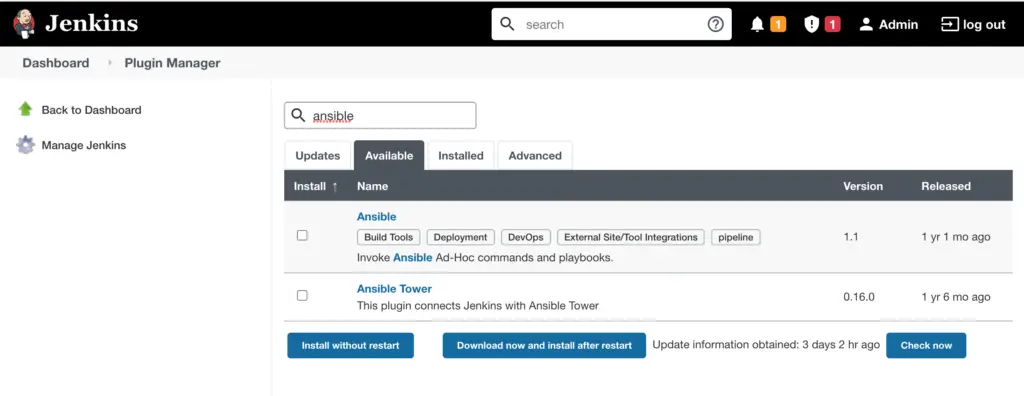
Search for Ansible plugin.
Install the Ansible plugin.
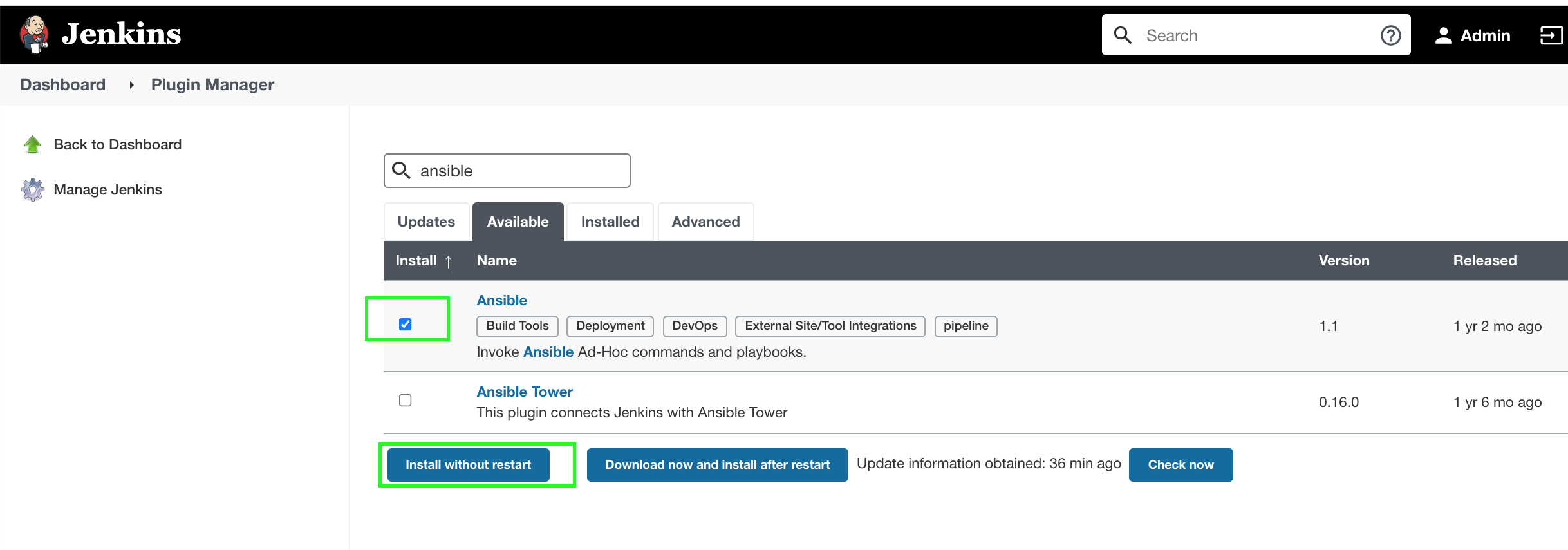
Choose the appropriate option.
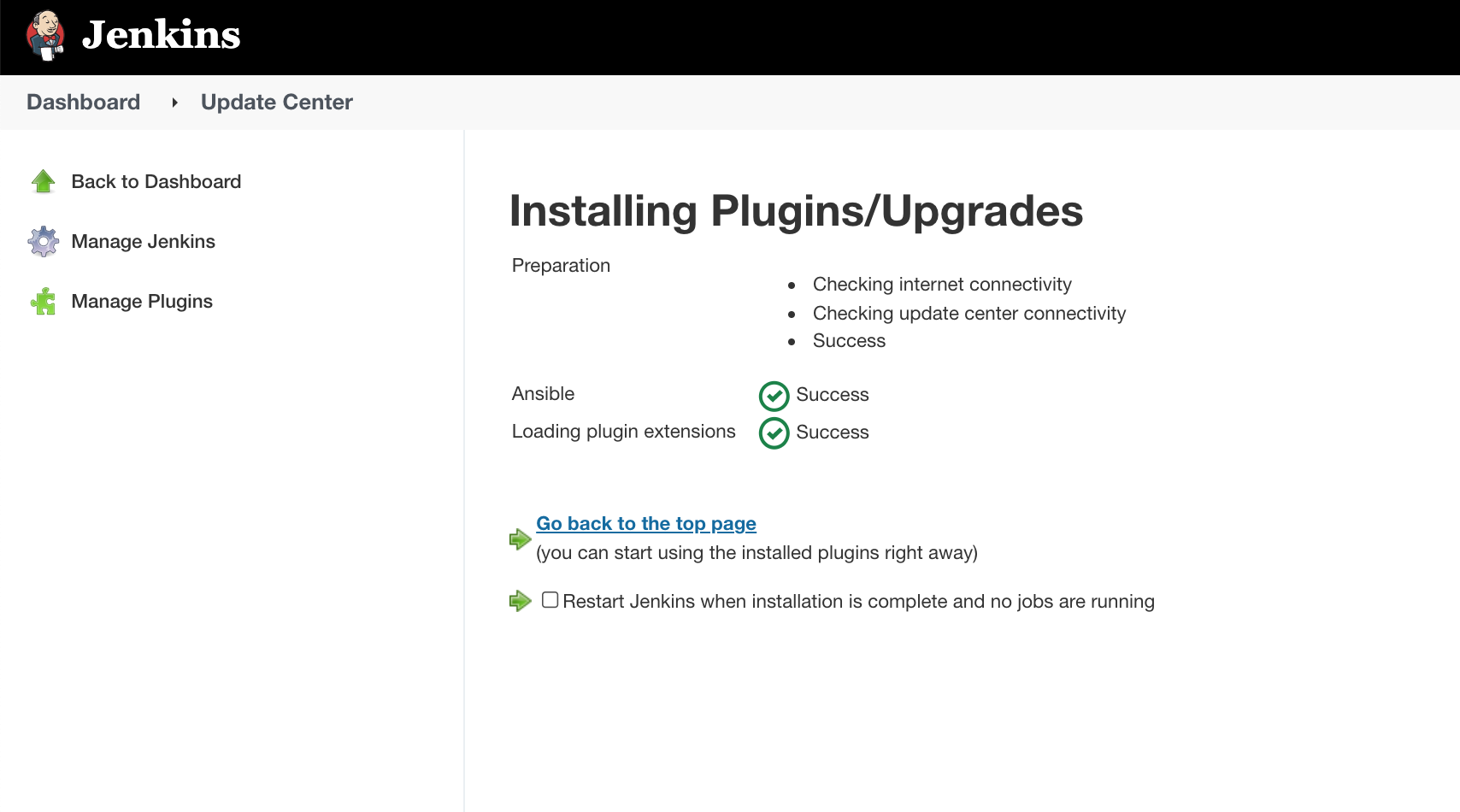
You can verify the status of installation from the Installed tab.
Now, install the Ansible on Jenkins master.
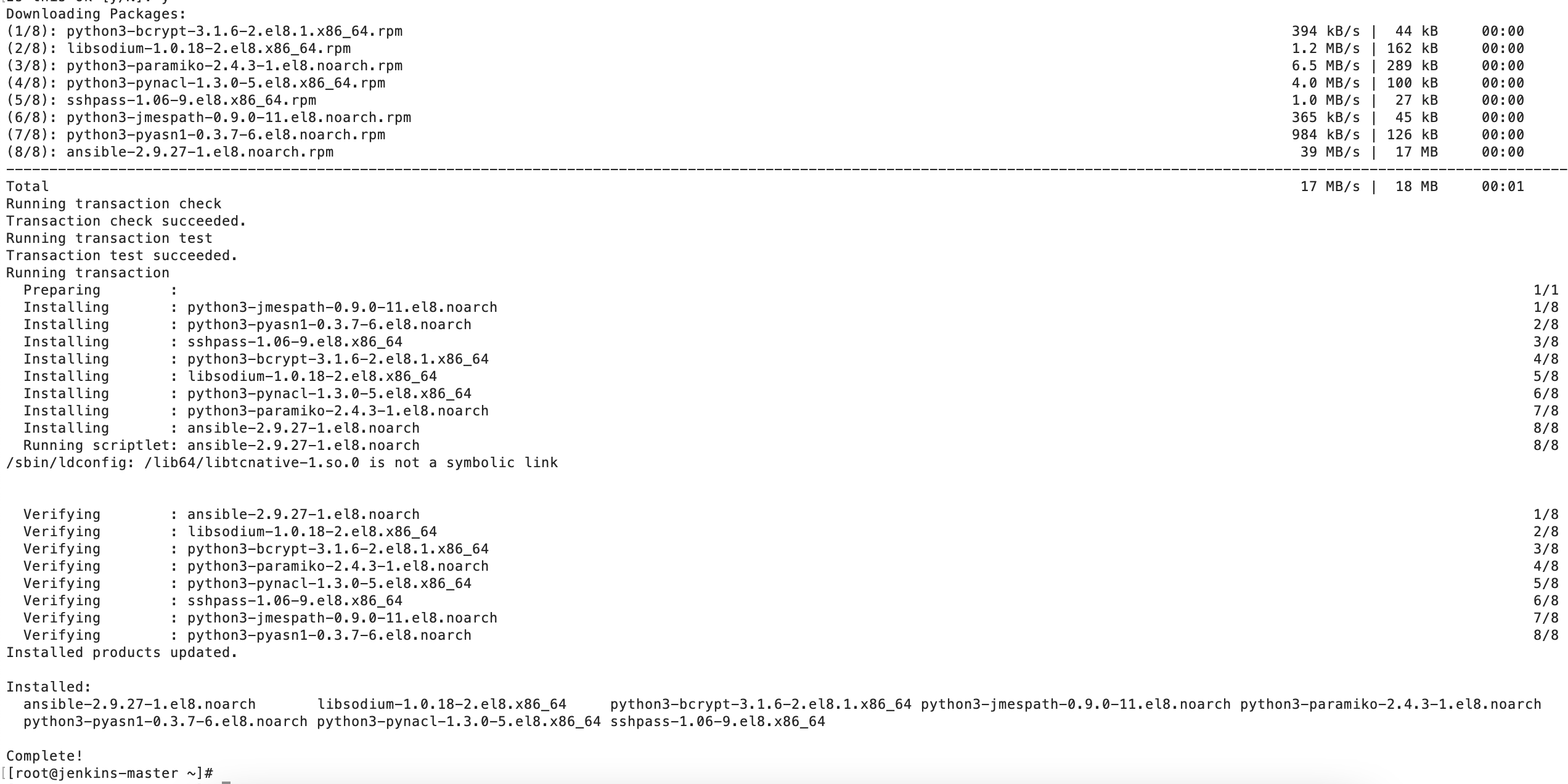
Step #2. Install Ansible package on Jenkins Master
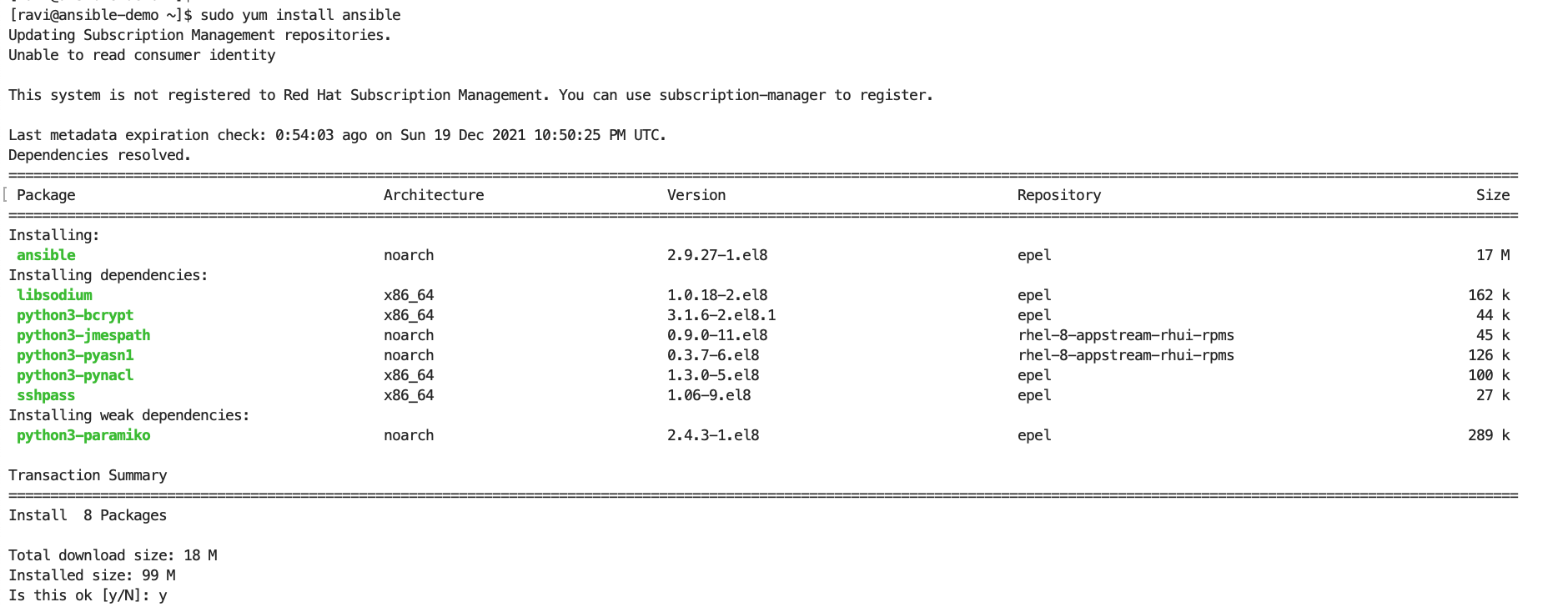
Install the ansible through your server’s package manager, such as yum, apt-get, etc.

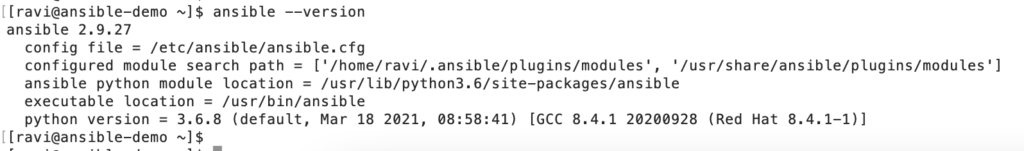
Verify Ansible Version.
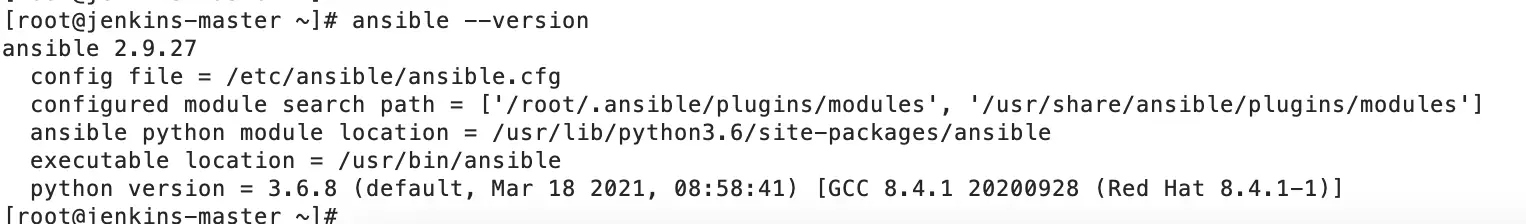
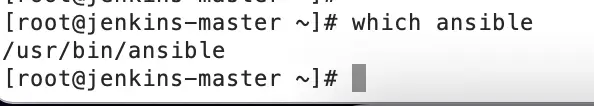
Find the Ansible location which we need to provide in Jenkins Tools configuration.
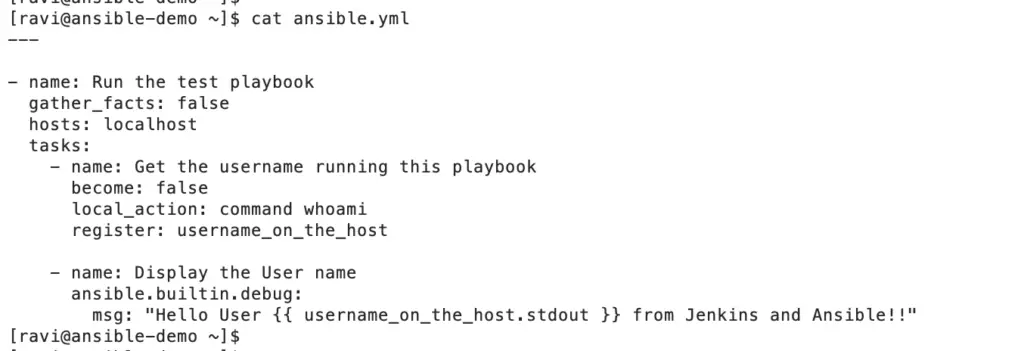
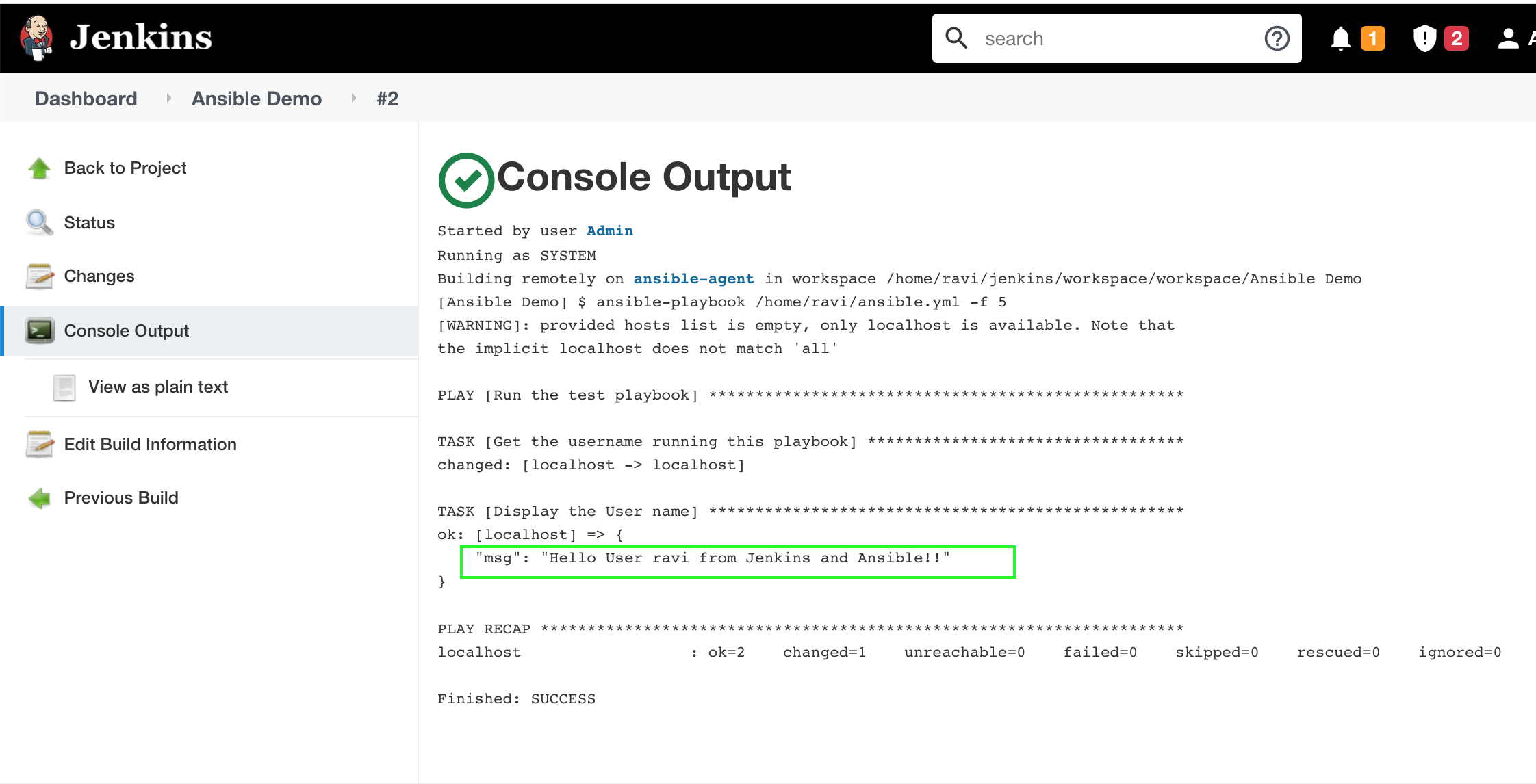
Create a test playbook ‘ansible.yml’ which prints the username.
---
- name: Run the test playbook
gather_facts: false
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- name: Get the username running this playbook
become: false
local_action: command whoami
register: username_on_the_host
- name: Display the User name
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Hello User {{ username_on_the_host.stdout }} from Jenkins and Ansible!!"Now, we need to configure Jenkins Tools Configuration to let Jenkins know the Ansible location on the server.
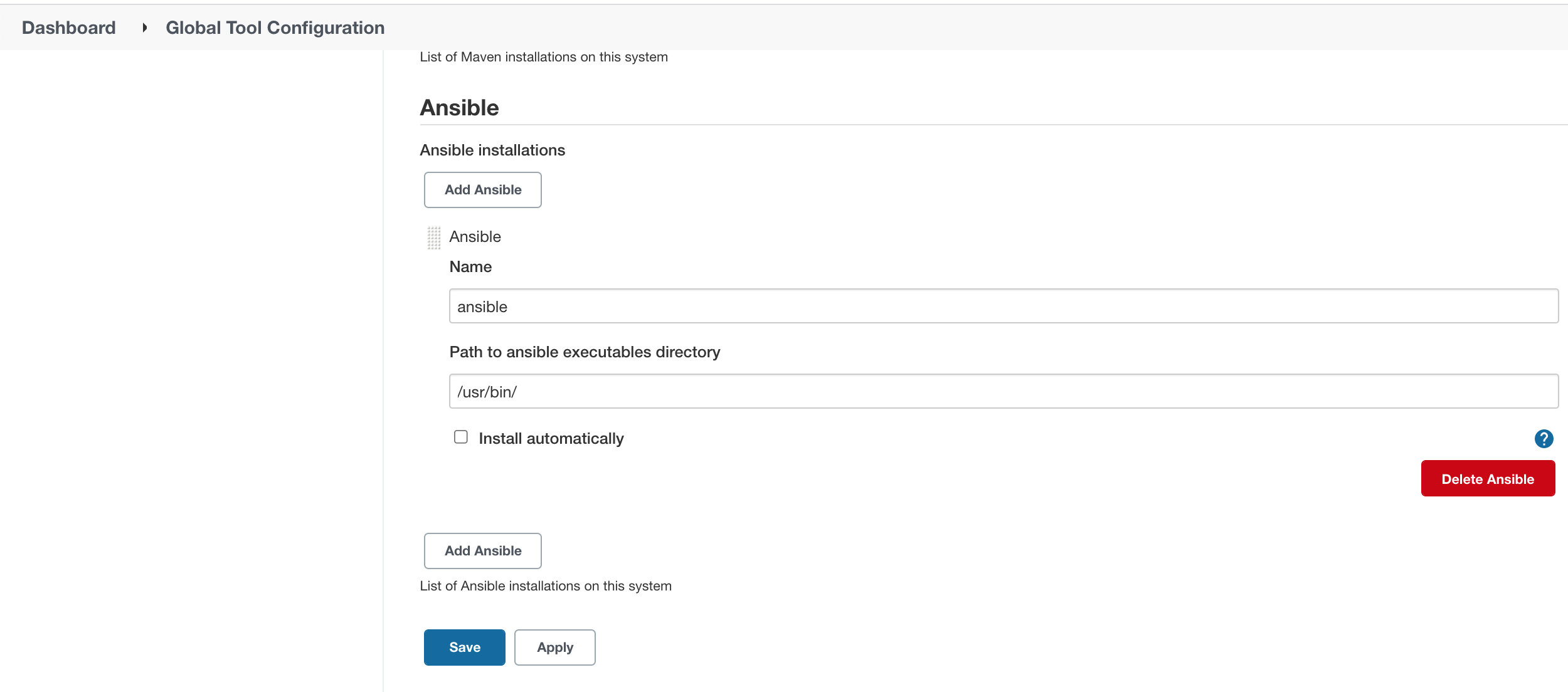
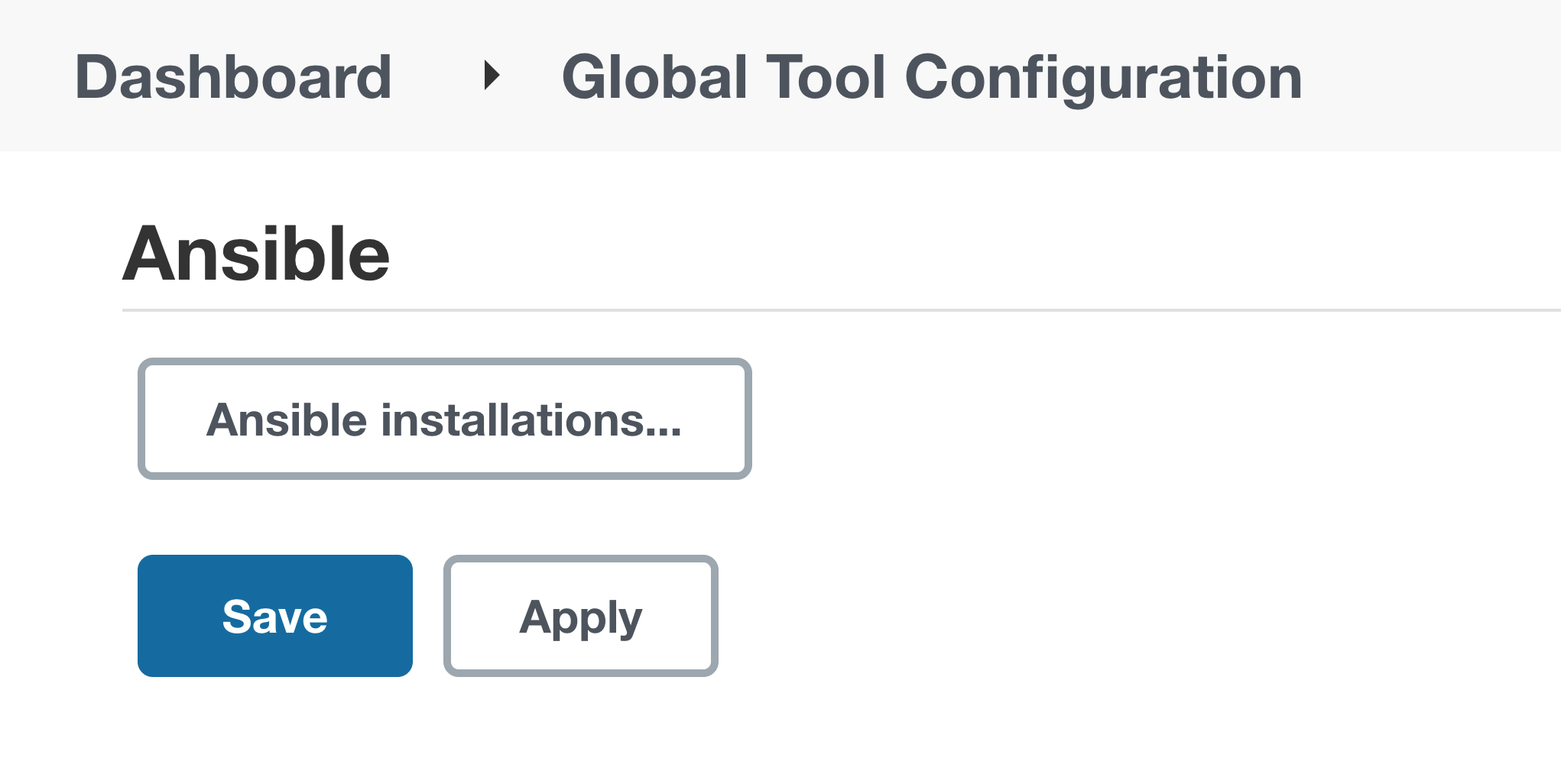
Step #3. Configure Ansible in Jenkins Global Tool Configuration
Go to Manage Jenkins –> Global Tool Configuration.
Configure the Ansible Tool Configuration.
Ansible installations > Add Ansible.
Provide the name; for example: ansible and /usr/bin/ to the Path to ansible executables directory space. This is the path we found when we executed ‘which ansible’ on the server.
Click Save button.
Now, once you have done the required configurations, you have two options of running the playbook through Jenkins jobs:
Step #4.1. Run Ansible Playbook as Jenkins Freestyle Job
Let’s move to Jenkins Dashboard
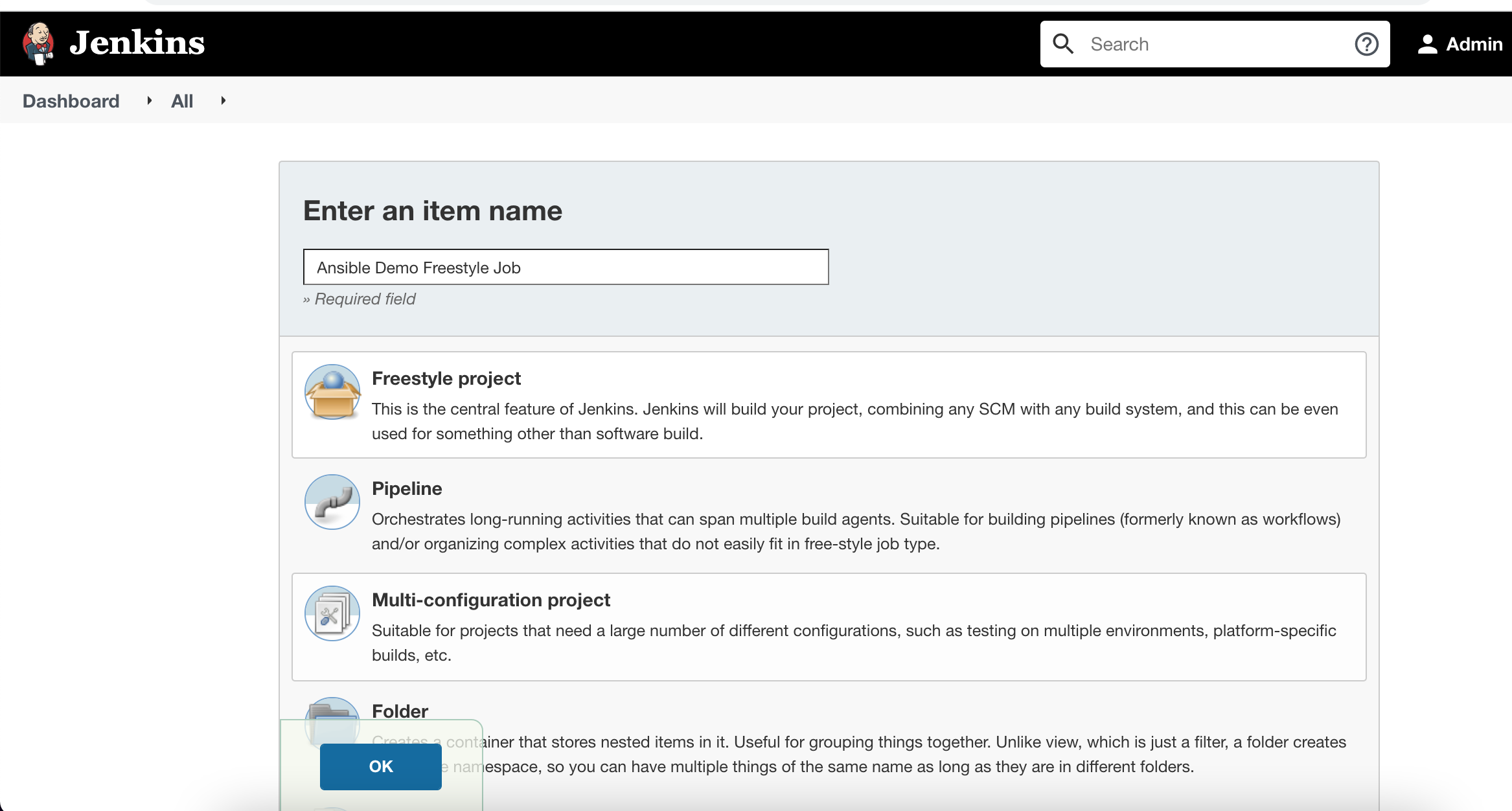
Create the ‘Freestyle Project‘
Click on New Item and provide Job details.
Configure the Job to run the Playbook.
Choose the ‘Invoke Ansible Playbook‘ option as Build Step.
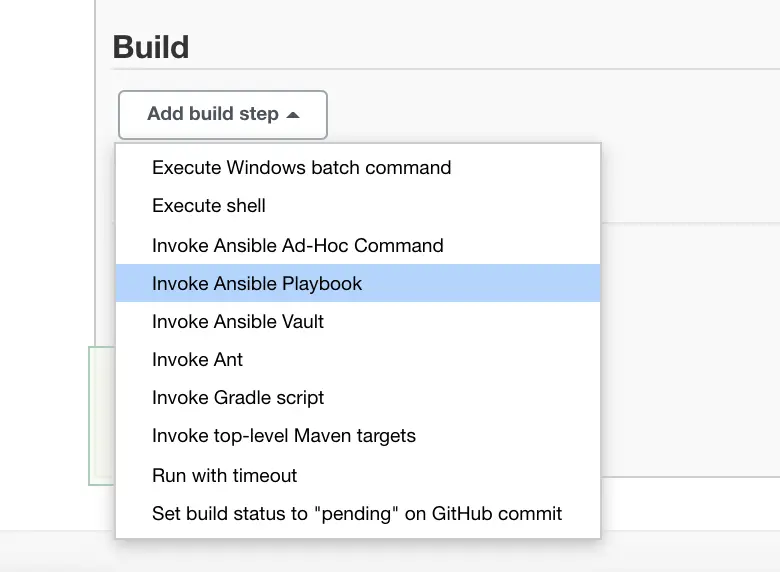
And configure the same playbook which was created to print the username.
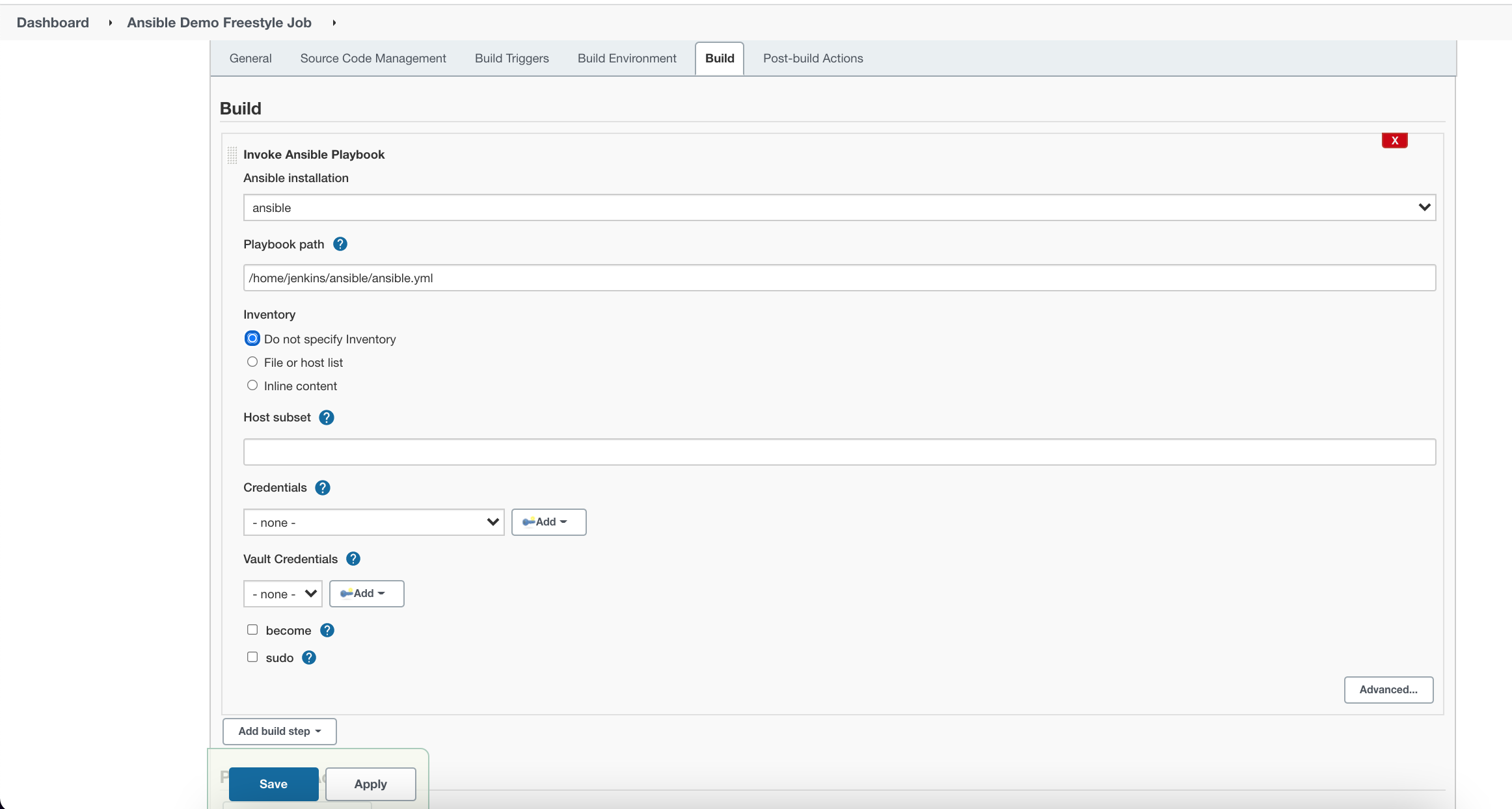
Save the Job and click on Build Now.
Verify the Console log.

Step #4.2. Run Ansible Playbook with Jenkins Pipeline Job
To run Ansible playbook with Jenkins Pipeline:
Create a Jenkins Pipeline Project
Click on New Item and provide Job details.
Configure the Pipeline script.
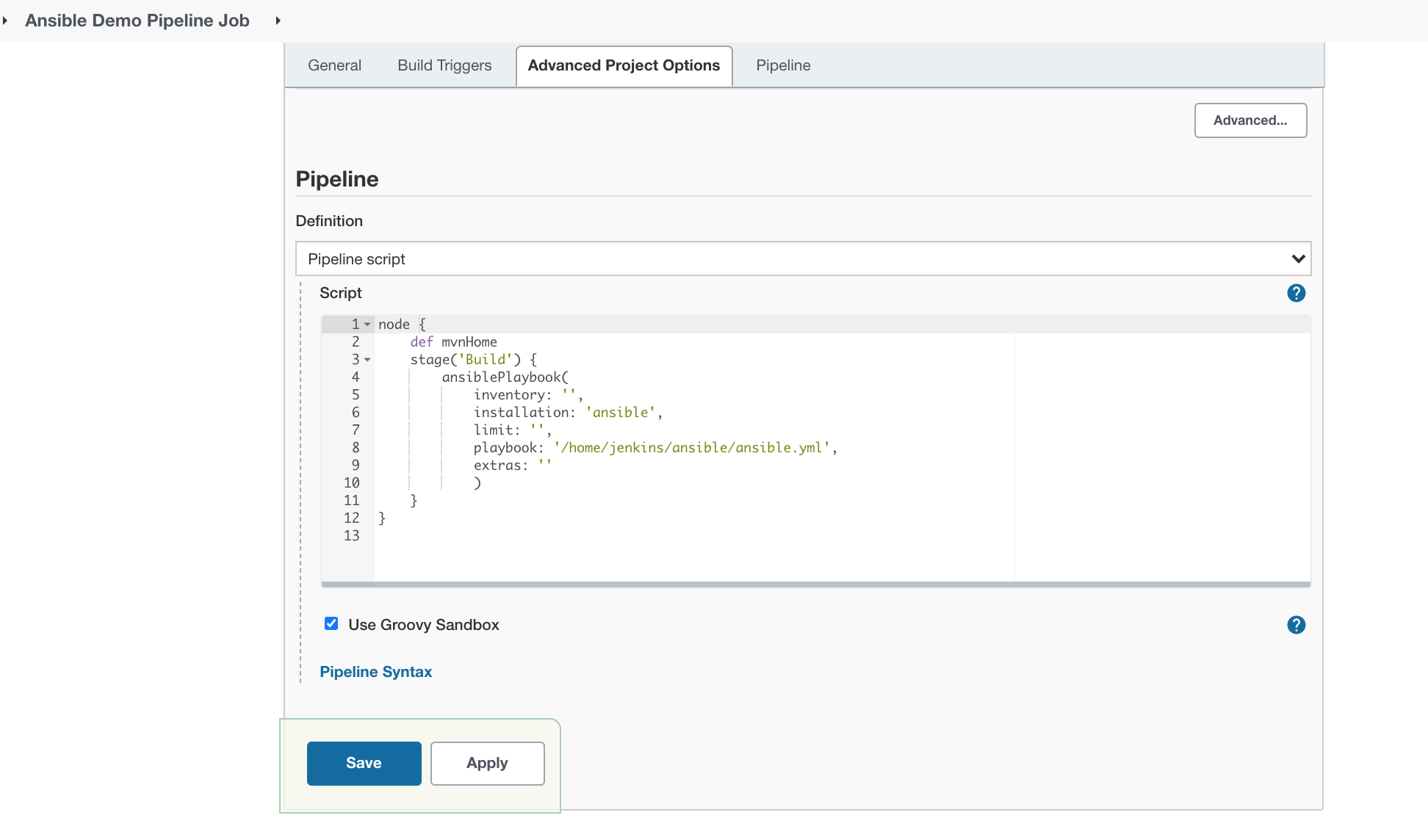
Here:
- inventory: ‘ansible inventory file’,
- installation: ‘Name of the Ansible tool which you had provided in Jenkins Tools configuration’,
- limit: ‘if need to limit it to any host where you want to run the playbook’,
- playbook: ‘name along with the path of the ansible playbook’,
- extras: ‘options and variables which you want to add’
Save the Job and click on Build Now and Verify the Console log.

Let’s move to the traditional way of running Ansible playbook through Jenkins freestyle or Pipeline job by executing Shell:
Method #2. Run Ansible Playbook through Jenkins by Executing Shell Command
Pre-requisites:
This time, instead of choosing the Ansible module as Build Step, choose the ‘execute shell’ as the build step.
Since the node was Linux node, I’ve used ‘Execute Shell’ method whereas, if you need to run the same on Windows machine, you need to use the ‘Execute Windows Batch command’
Choose ‘Execute Shell‘ as Build Step
Provide the appropriate ansible-playbook command along with required parameters, I’ve just used the basic one:
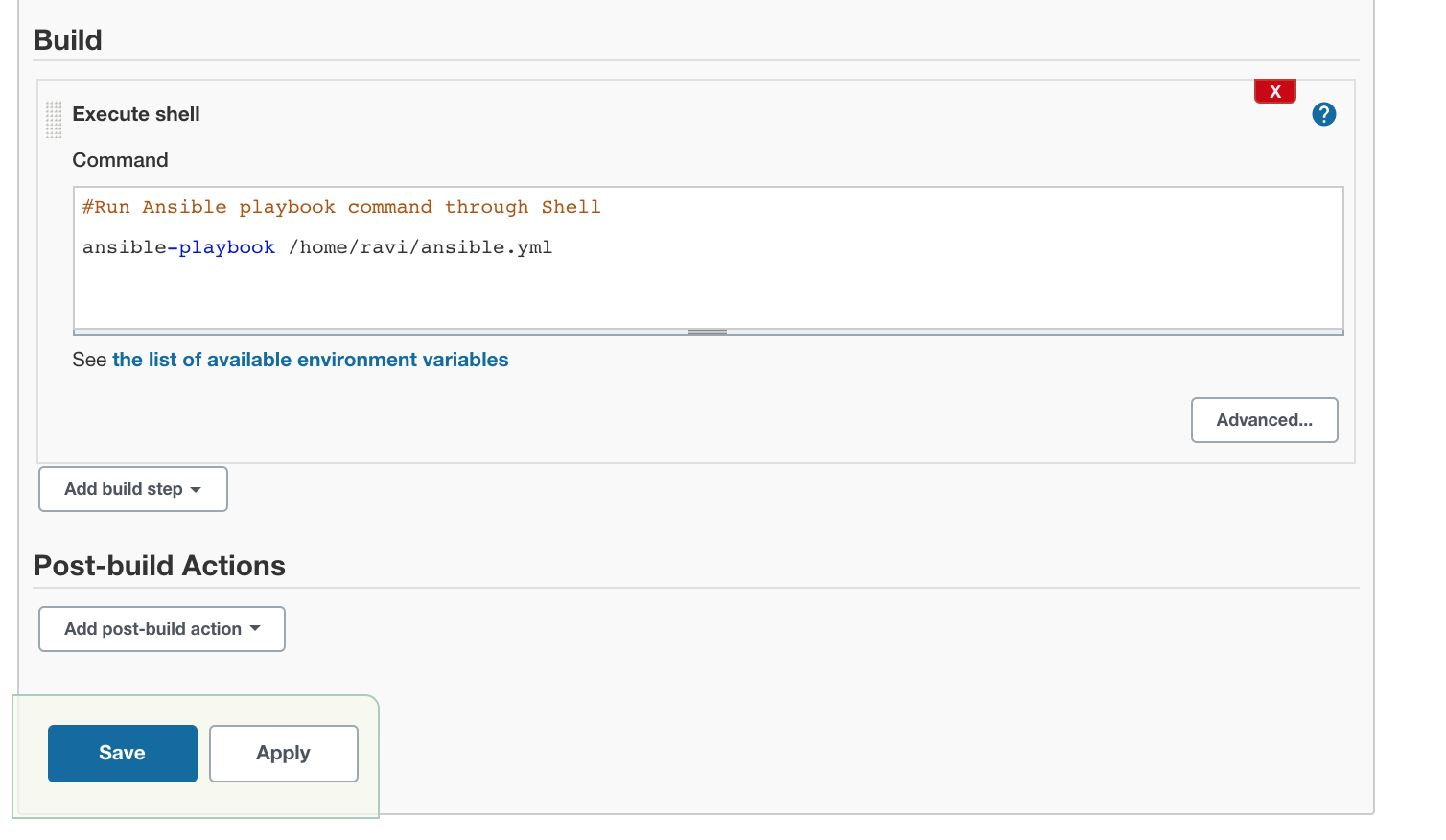
Save the Job and click on Build Now and Verify the Console log.

All good.
You now know how to integrate Ansible with Jenkins after installing/configuring Ansible on Jenkins master.
However, you might need to explore another option to run the Ansible playbook from the Jenkins Node machine which has Ansible installed on it.
So, let’s check out this option as well:
Method #3. Run Ansible Playbook from Jenkins With a Dedicated User and Jenkins Node
I received a request from one of our readers on our post for the in-depth Jenkins setup, who was facing an issue with running the Ansible playbook from Jenkins Node with a dedicated user on a remote host as per his project requirements.
Though the best practice is to configure Ansible on the Master node through Global Tool Configuration; in some scenarios, we need to consider these kinds of scenarios as well.
So, the request has the below requirements:
- Jenkins should be able to run Ansible playbook
- There shouldn’t be any ansible installation or configuration on Jenkins Master node
- Ansible playbook should be executed through the dedicated user
- Jenkins agent/node should have these configuration and Job should run on the specific node only
Pre-requisites:
For this demo, I have removed the Ansible from “Jenkins Global Tools Configuration“
Step #1. Install Ansible Plugin
We have already installed the Ansible plugin, so we can go to the next step.
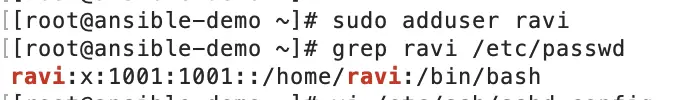
Step #2. Create Dedicated User on Linux Machine
Now, log in to the Linux server
For this demo, I have used a Linux machine and will turn this machine into Jenkins Node. If you need to run the same scenario on a Windows machine, then please follow our guide on Jenkins Windows Slave setup.
Add Dedicated User as per the requirement and verify it.
Provide Sudo access to my user since its a blocked instance.
Login through new user.
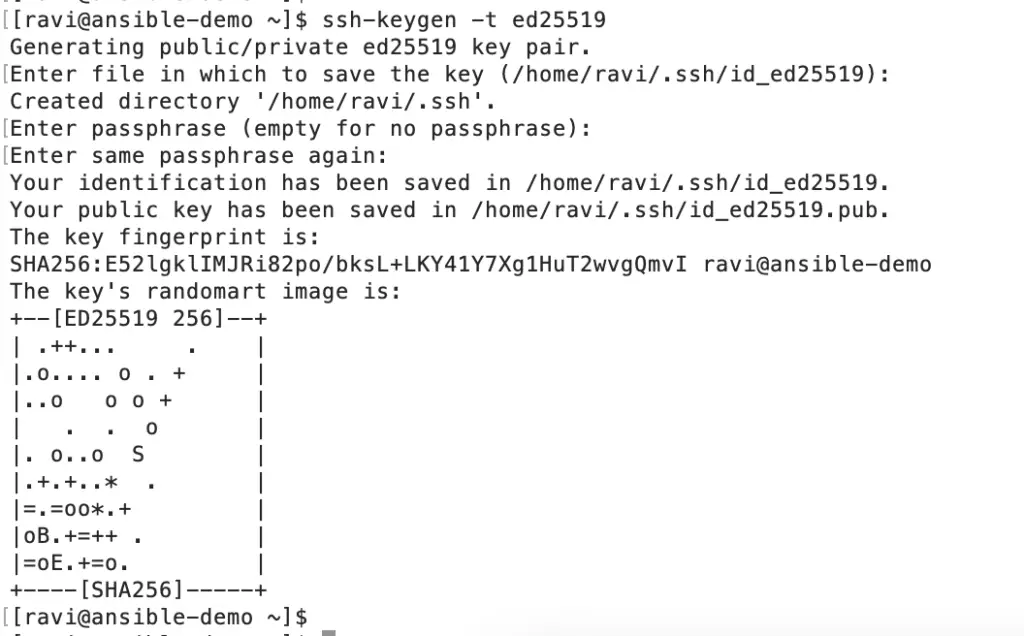
Create ssh key for the user.
Create the authorized key and provide appropriate permission.
This is the most important step in order to establish ssh connection based on keys.
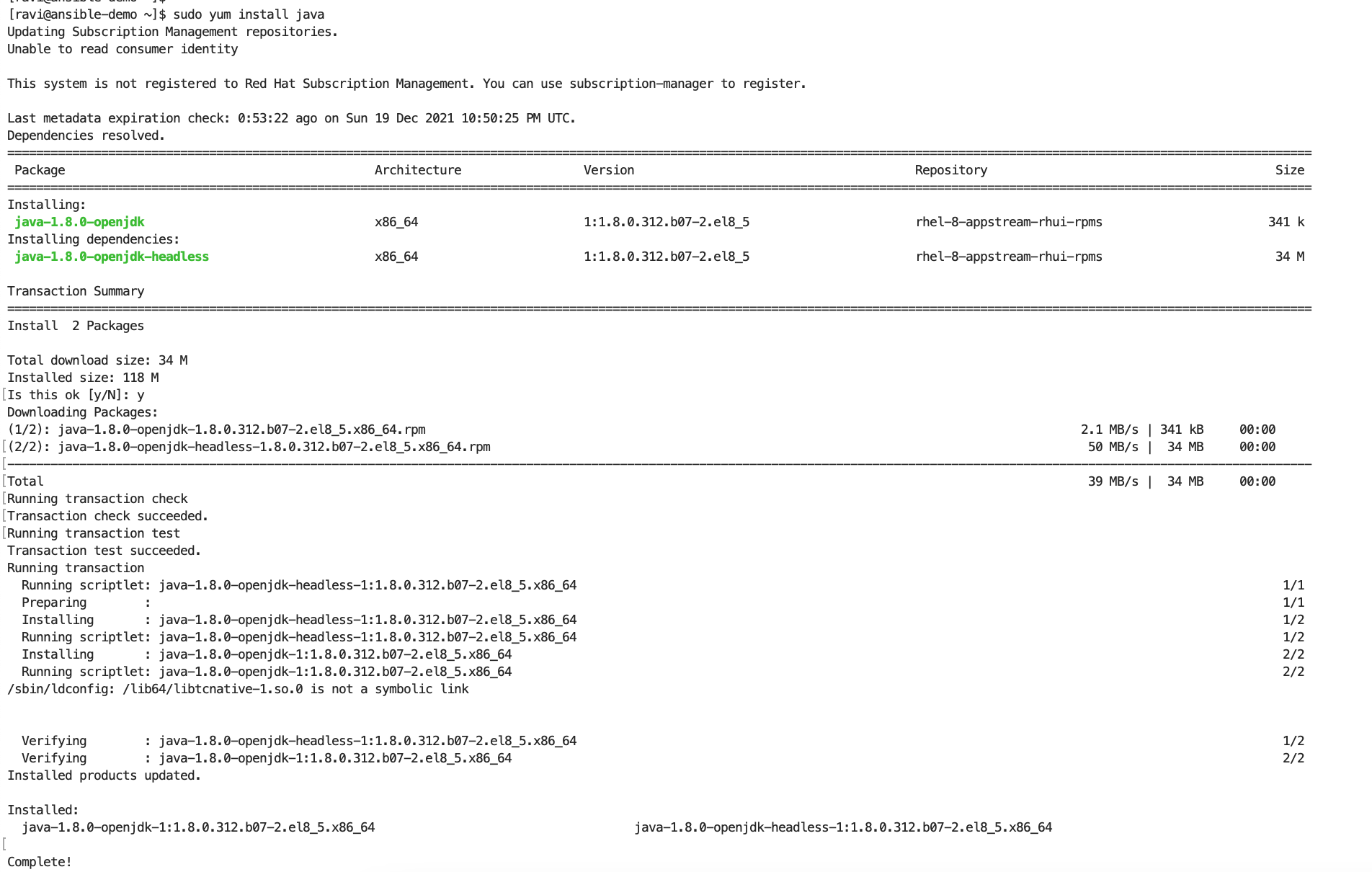
Step #3. Install Required Java and Ansible Through Yum
(Or, with your relevant package manager)
Install the prerequisite Java.
Verify Java Version.
Install Ansible on Jenkins Node.
Verify Ansible Version.
Step #4. Create test Ansible playbook
Create playbook which records the current username and print it.
Change playbook permissions.
Step #5. Create Jenkins Node directory
Create a directory for Jenkins to run all the nodes activities on this server.
This completes the server related activities.
Now, let’s go back to Jenkins and add the newly created node to run all the ansible playbooks.
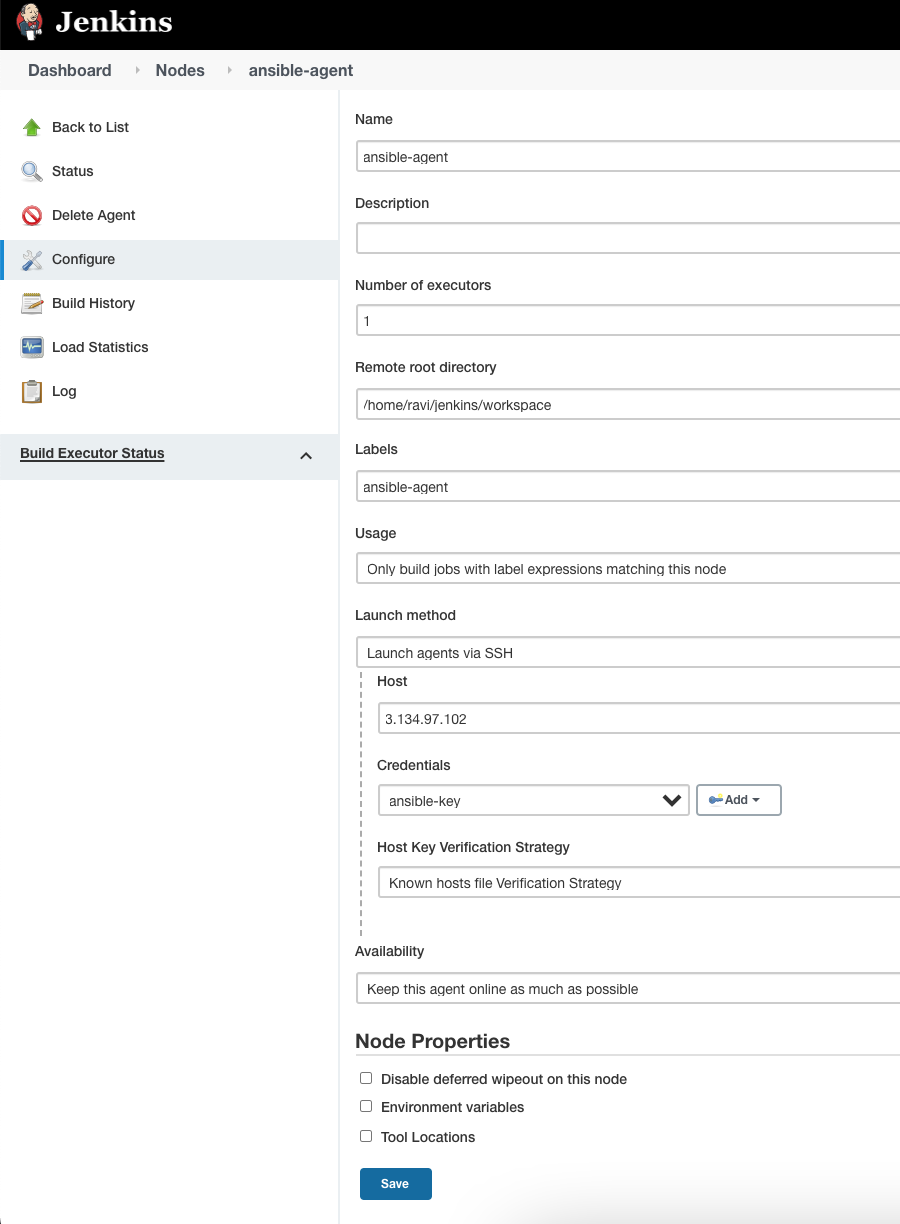
Step #6. Add Jenkins Node
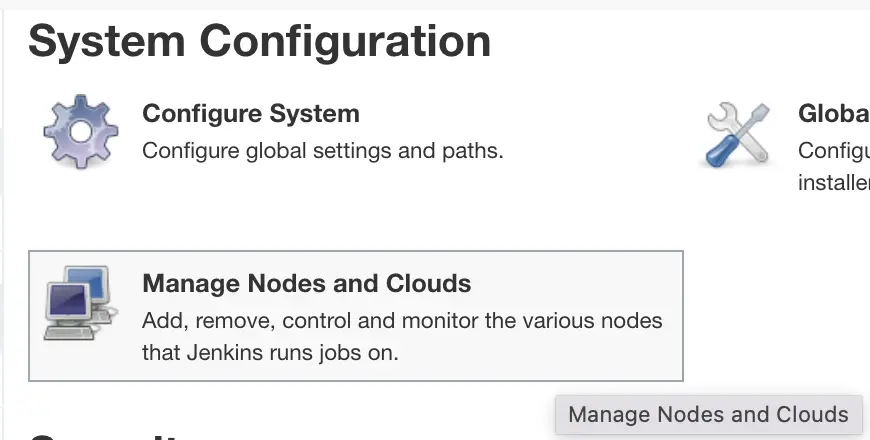
Go to ‘Manage Jenkins‘
Go to ‘Manage Nodes‘
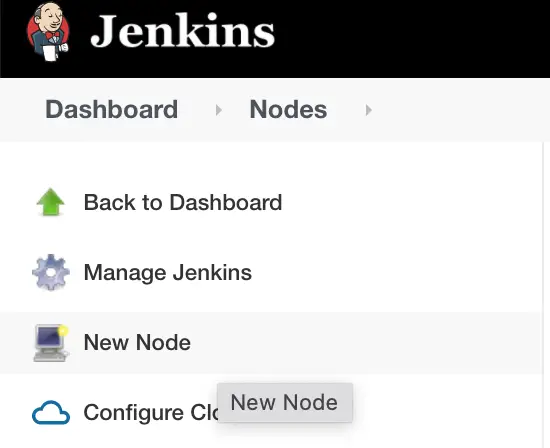
Click on ‘New Node‘
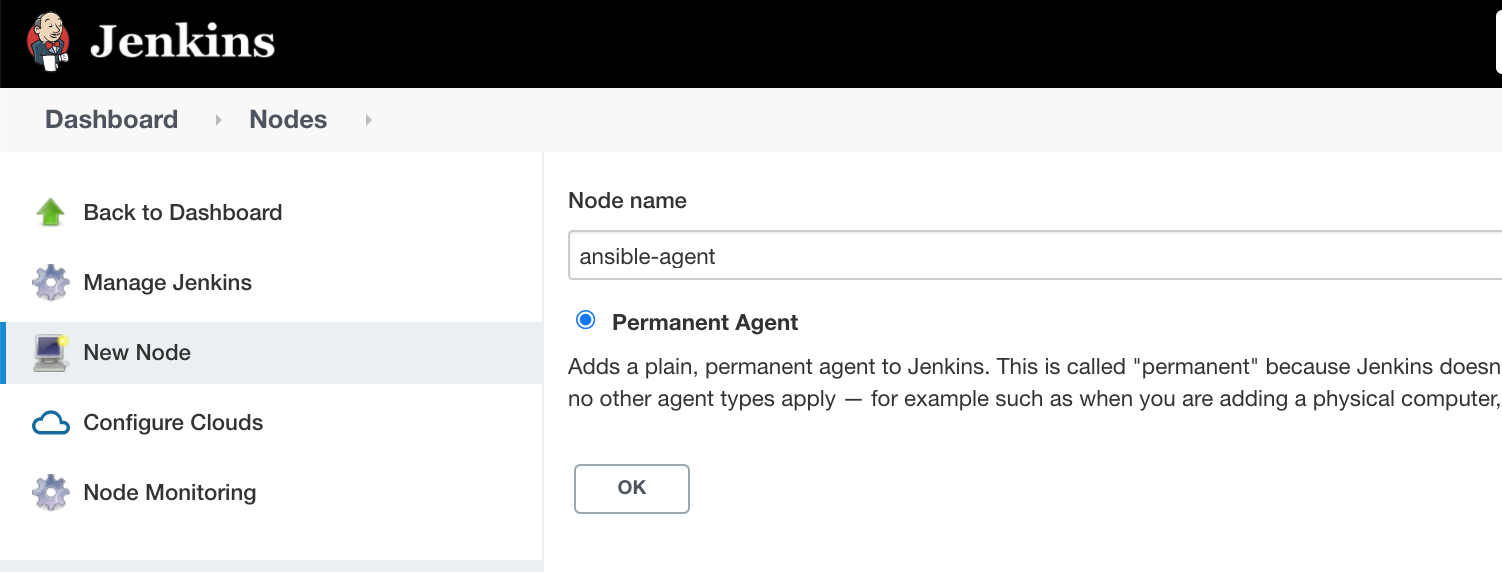
Provide Node details and click OK.
Provide the relevant configuration.
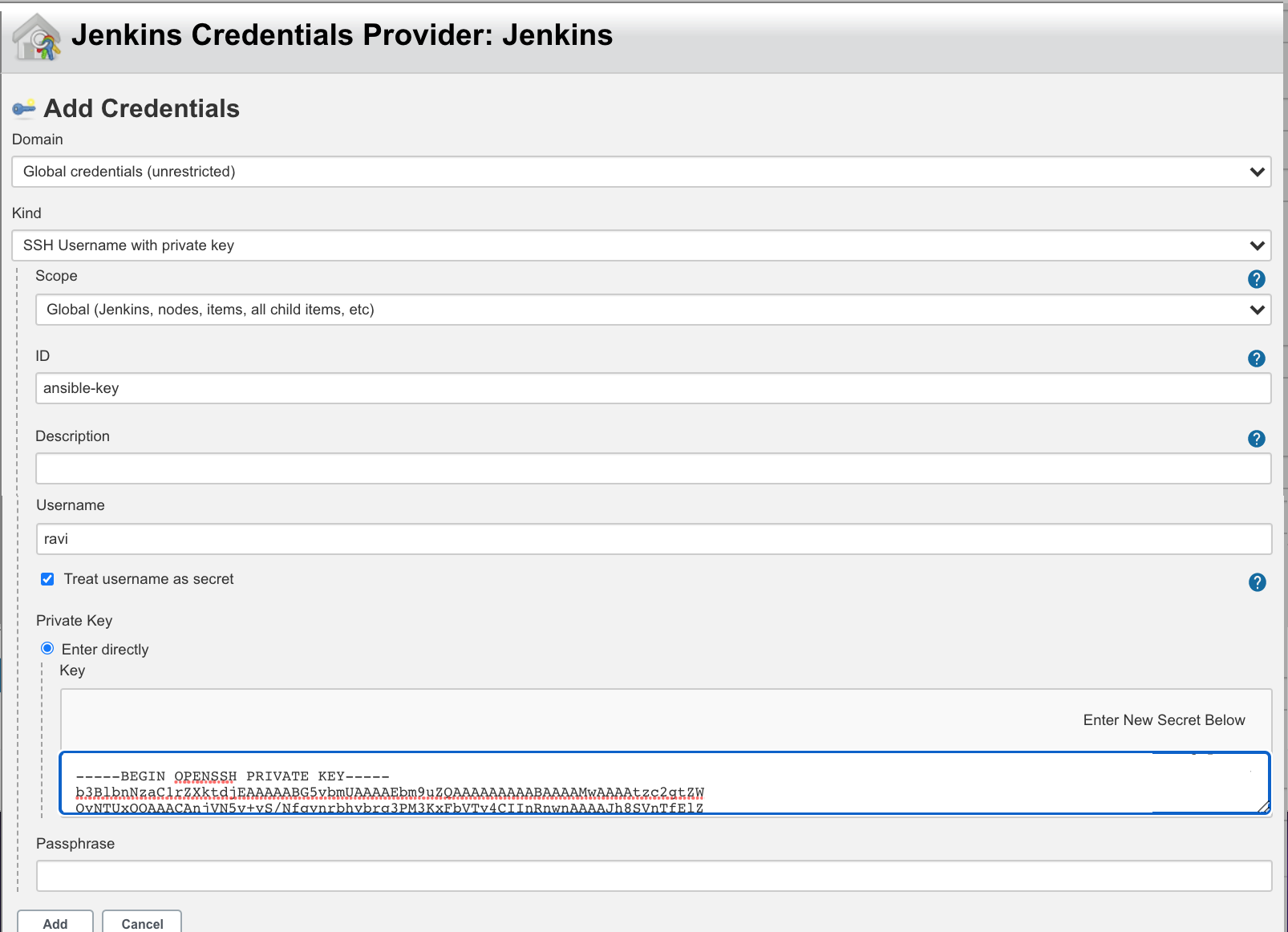
** Add the Credentials – choose ‘SSH Username with private key’ option and provide Linux server’s user name and Private key
Click on Add and select the same credential on the Agent Configuration page.
Click on Save. And click on Launch agent.
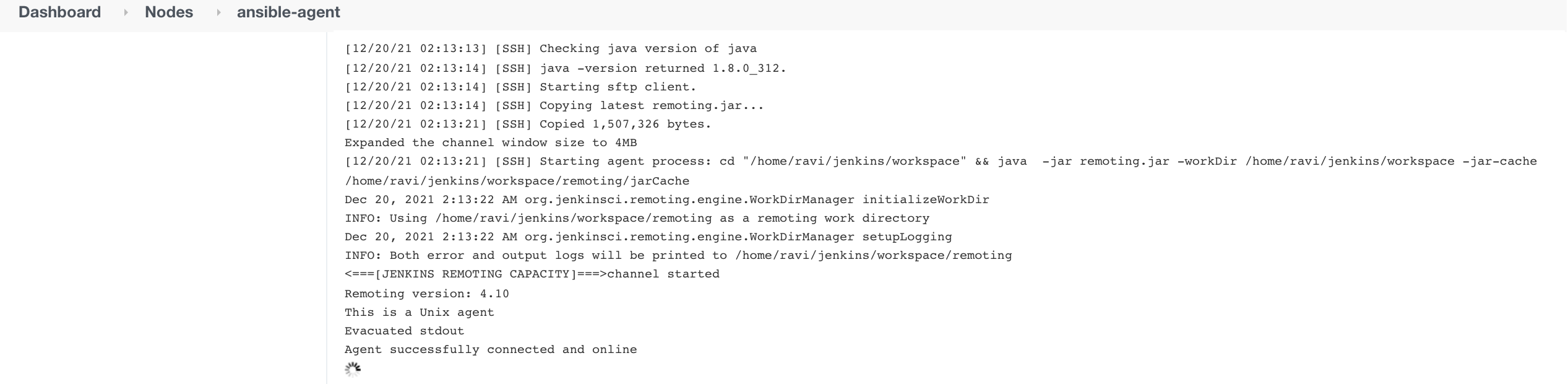
Now, proceed for the Jenkins Job creation to run the Ansible playbook on the newly added node/agent.
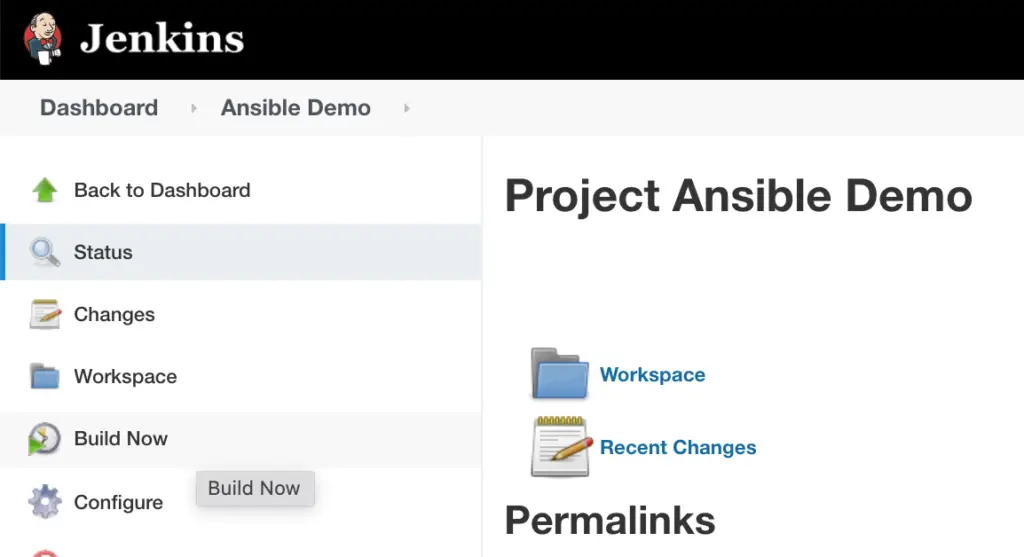
Step #7. Create Jenkins Job
Click on New Item and provide Job details.
Configure the Job.
Make sure to restrict this job to run against the Ansible agent/slave/node only.
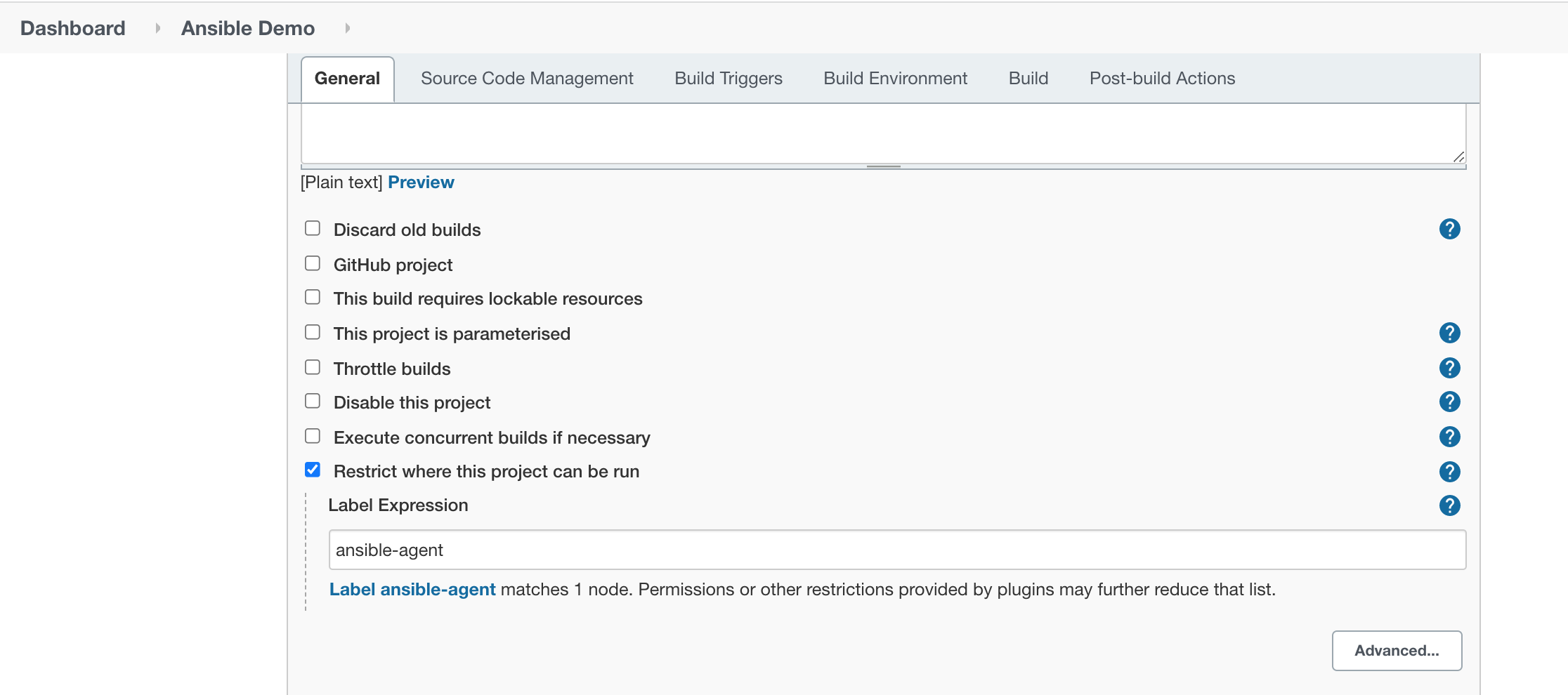
And choose the ‘Invoke Ansible Playbook‘ option in Build.
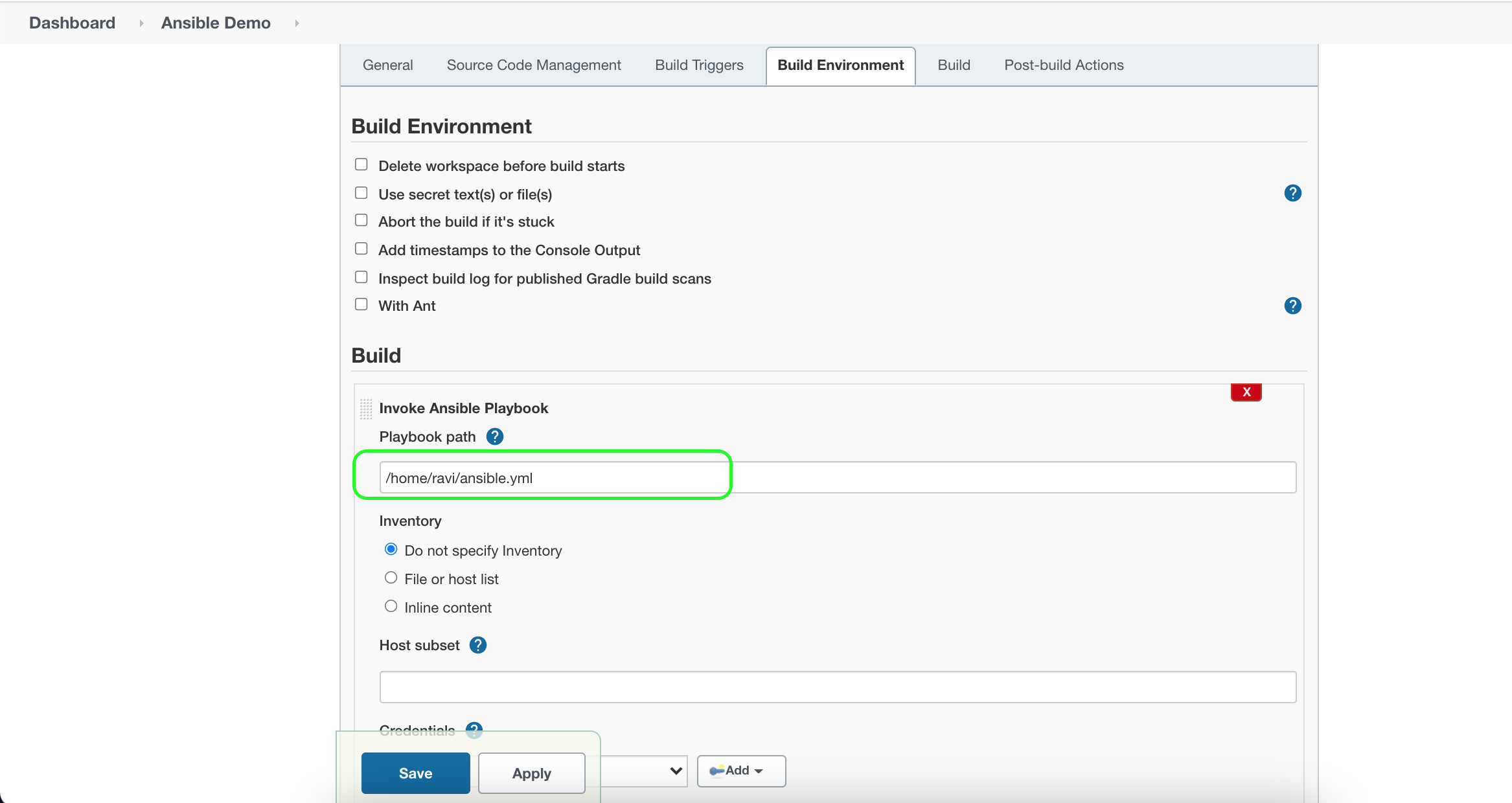
Save the Job and then click on Build.
Check the Console log to verify the execution.
With this method (#3), there is No need to configure Ansible on the Master server or update Jenkins Tool configuration, just install the plugin.
You can use this approach for both Jenkins Freestyle job as well as a Pipeline job.
You can escape the installation of the plugin as well if you need to execute ansible-playbook as a shell/batch command.
As I mentioned before, this is not the recommended way to use Ansible with Jenkins but sometimes turns out to be a very useful alternative in restricted environments.
All done. You should now be able to run the Ansible playbook with a dedicated user from the node server.
Wrapping Up
Okay, there you have it!
You now know three different ways to run the Ansible playbook from Jenkins.
If you get stuck with any of the methods shown on how to integrate the Ansible Playbook with Jenkins, drop a comment below.
So, which method did you opt for in the end?
If you like this guide, do share this on LinkedIn and subscribe to our free newsletter. You can also consider following us on our LinkedIn page where we regularly share tips and tricks for DevOps engineers.
Keep the quest on!









This is interesting, but I like to develop and test playbooks outside of jenkins, commit them to a version control system like github/, then have Jenkin check out the repository and run the commands defined in the Jenkins file.
Have you written an article about that use case?
Hi @ikomrad,
Thanks for the feedback.
I’ve not written an article on this topic yet but have used the same several times with my projects.
Basically, if you are using AWX tower, then you can set up the Projects and Dynamic inventory, where you can use gitlab/github/or any other VC to store your ansible roles, playbooks, and inventories.
Or if you are using standalone ansible, then just create the repository in your favorite version control and configure the ‘Source Code Management’ in Jenkins pipeline/Job with the repository details.
Configure the Build triggers and then use one of the methods provided in this article to run your ansible-playbook.
Please do give it a try and let me know in case of any issues.
Happy learning !!
This blog is great i really like studying your posts.
Keep up the great work! You know, lots of individuals are hunting round for this info, you can help them greatly.